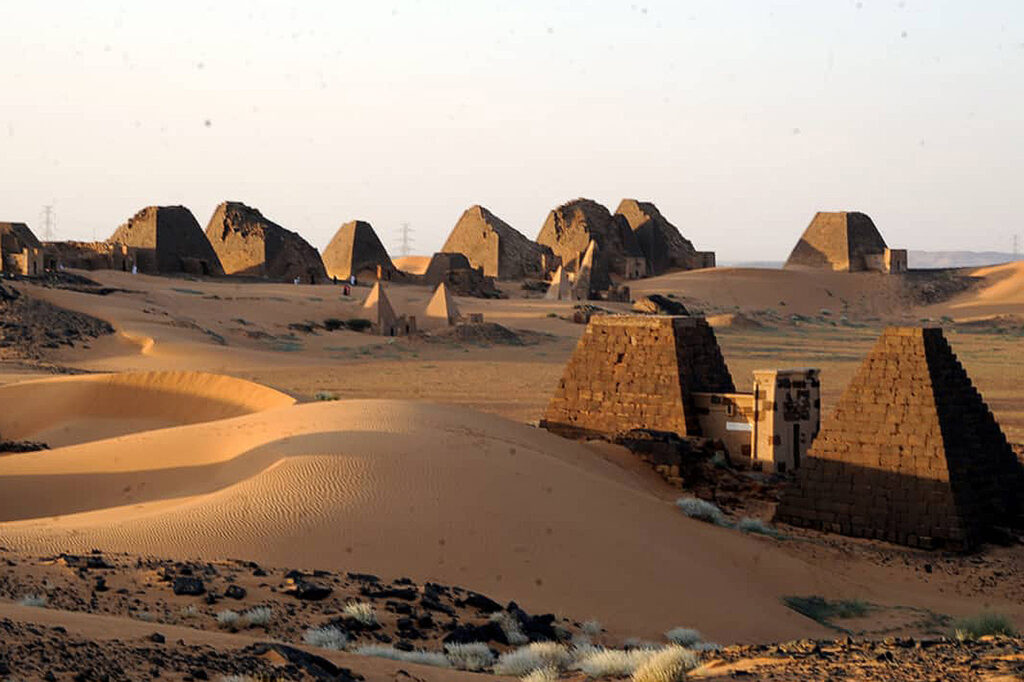
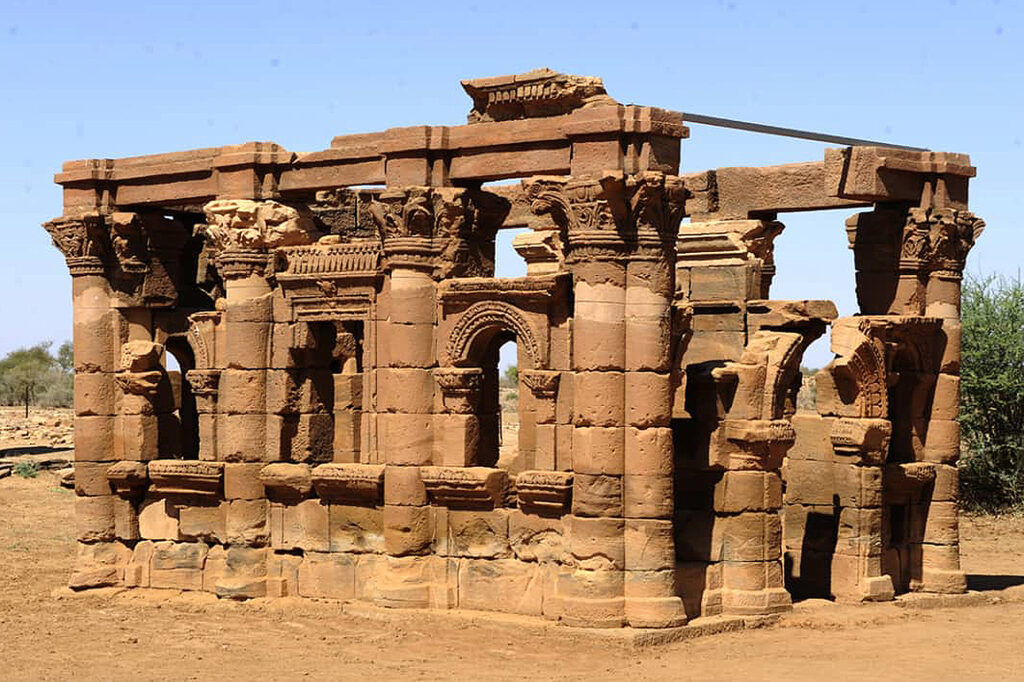
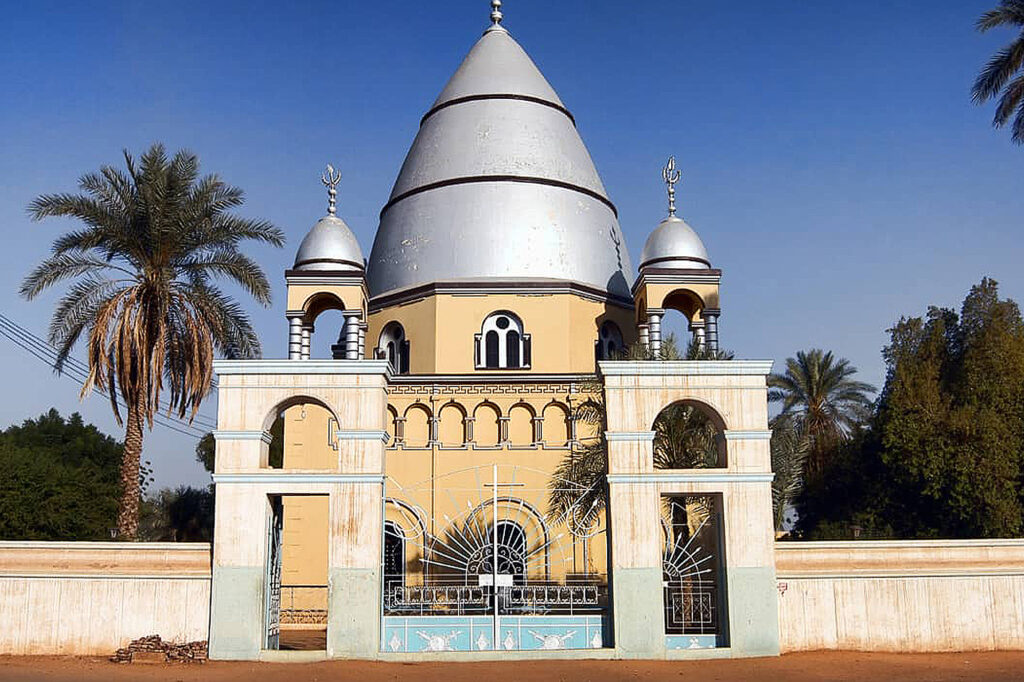
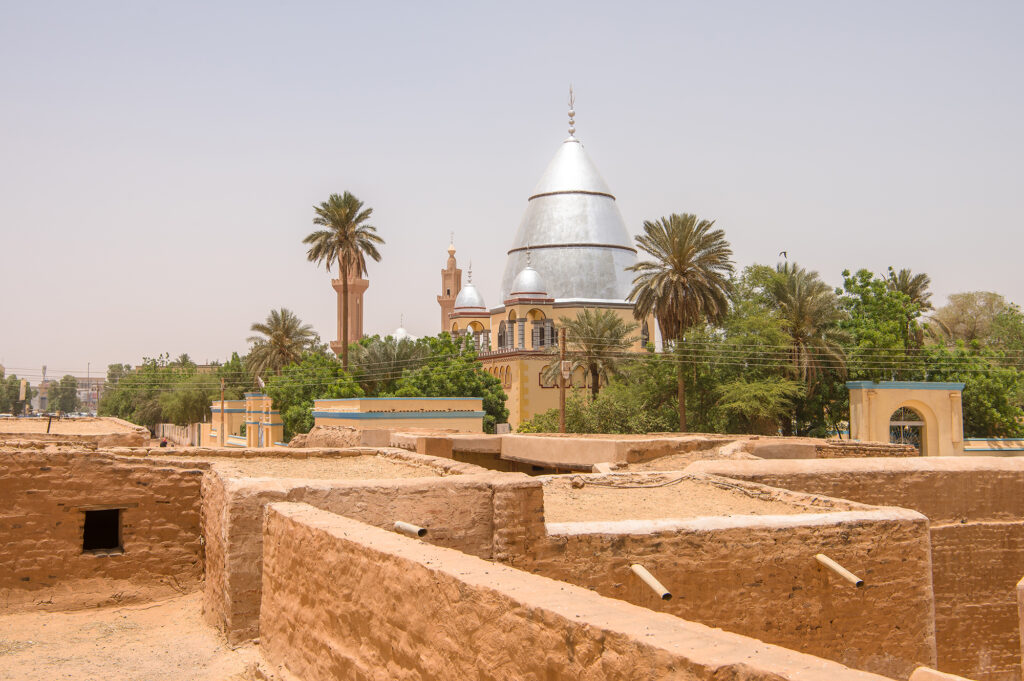
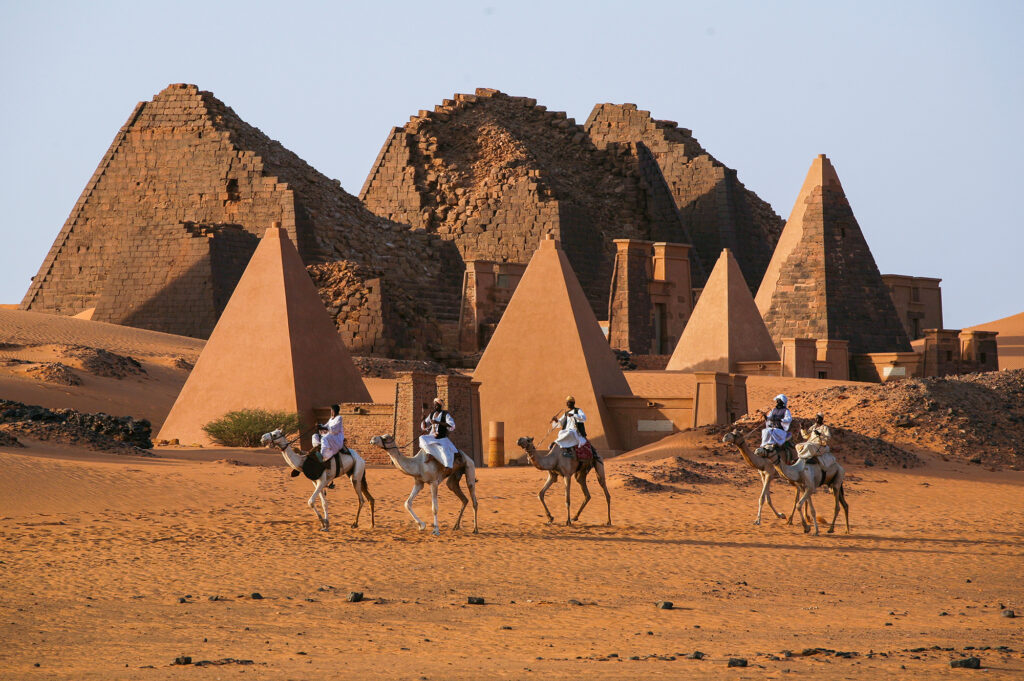
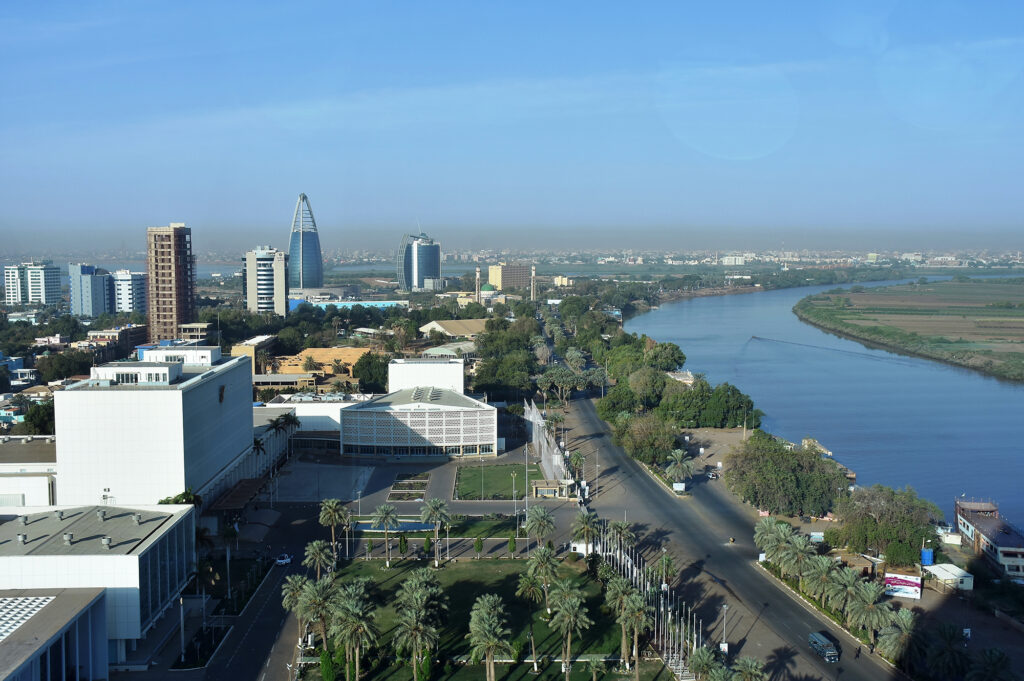
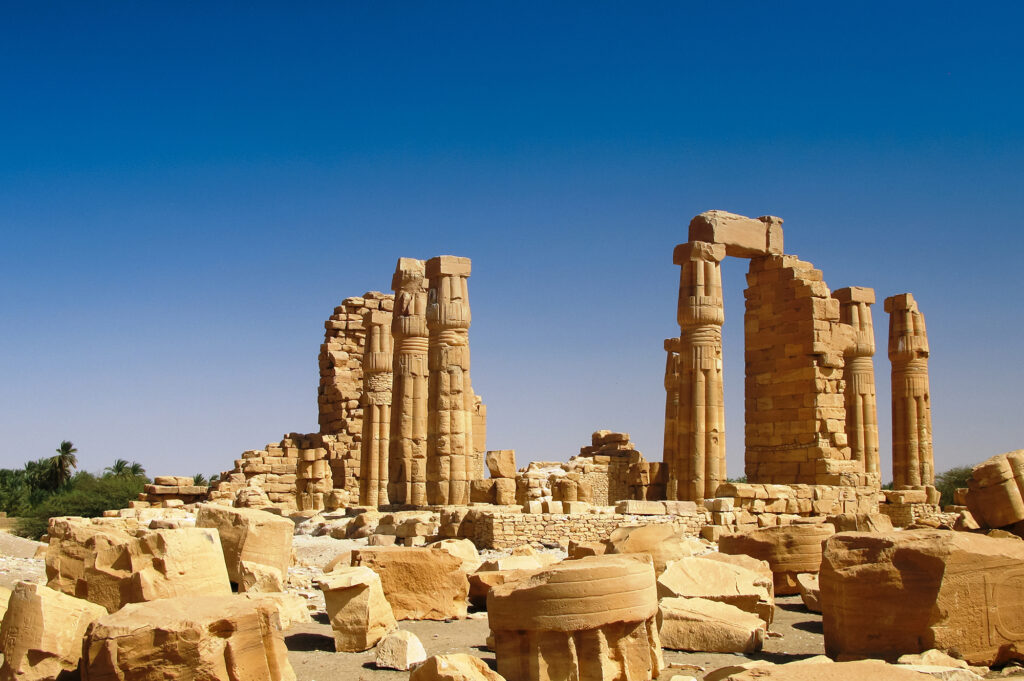
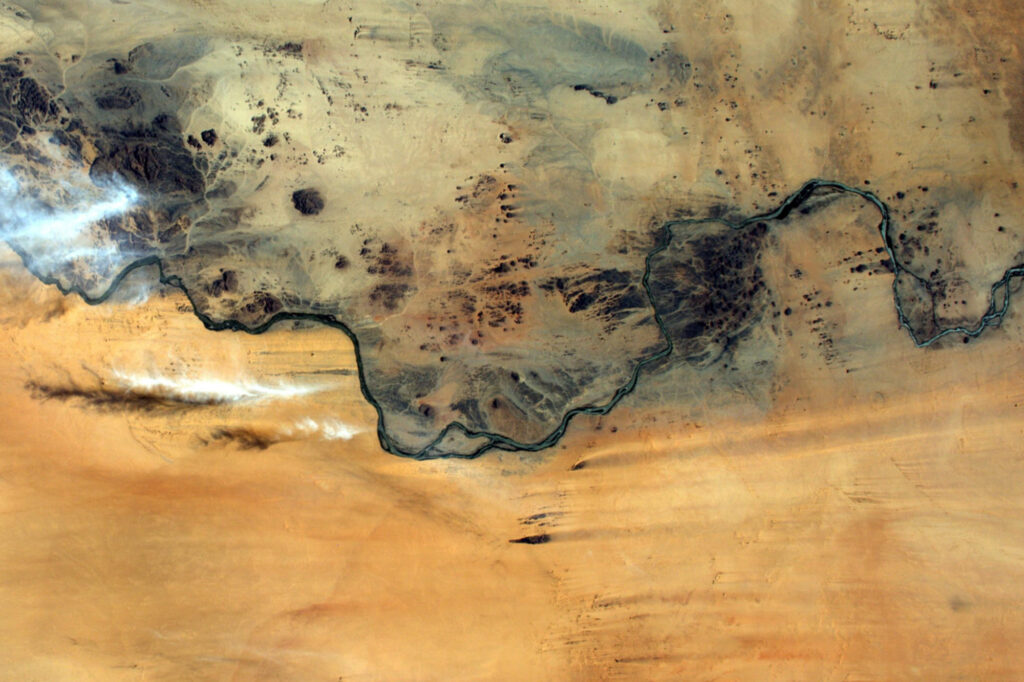
Discover Sudan
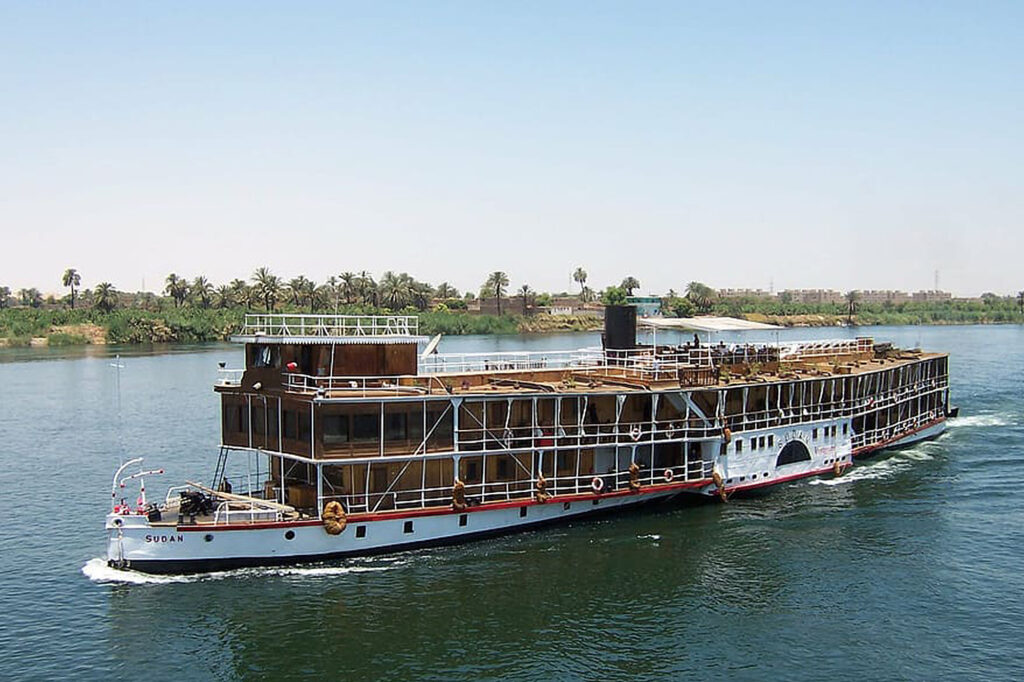
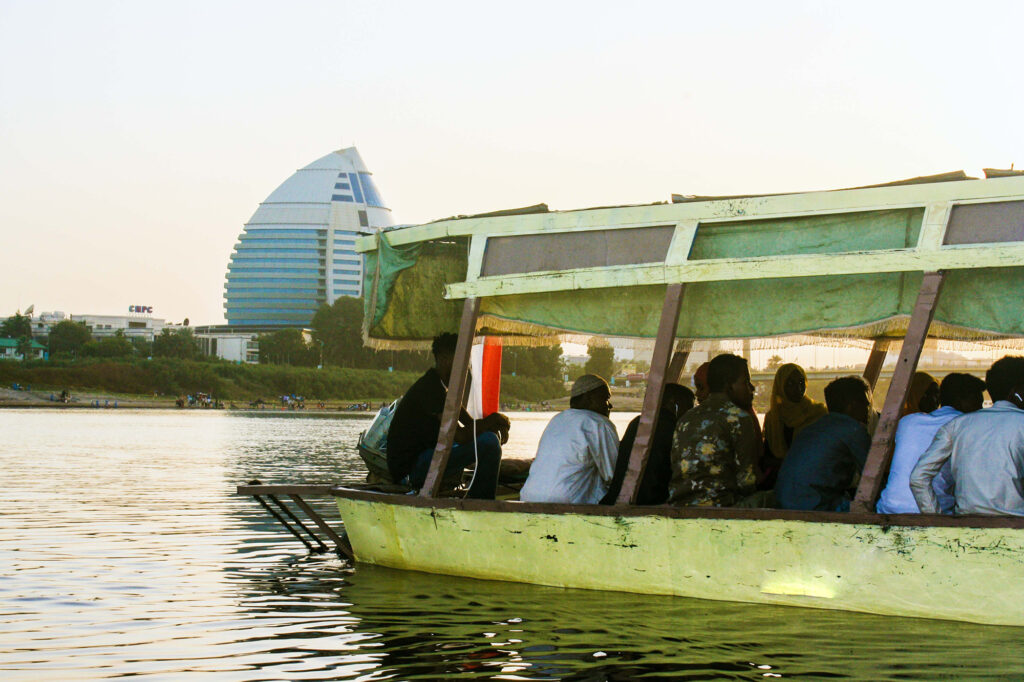
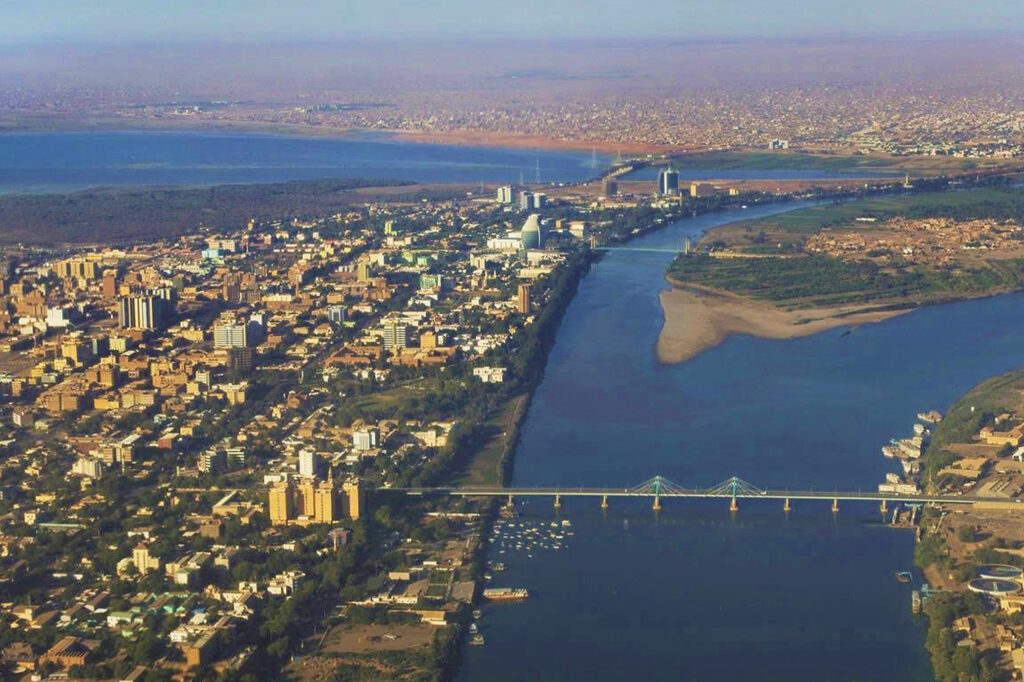
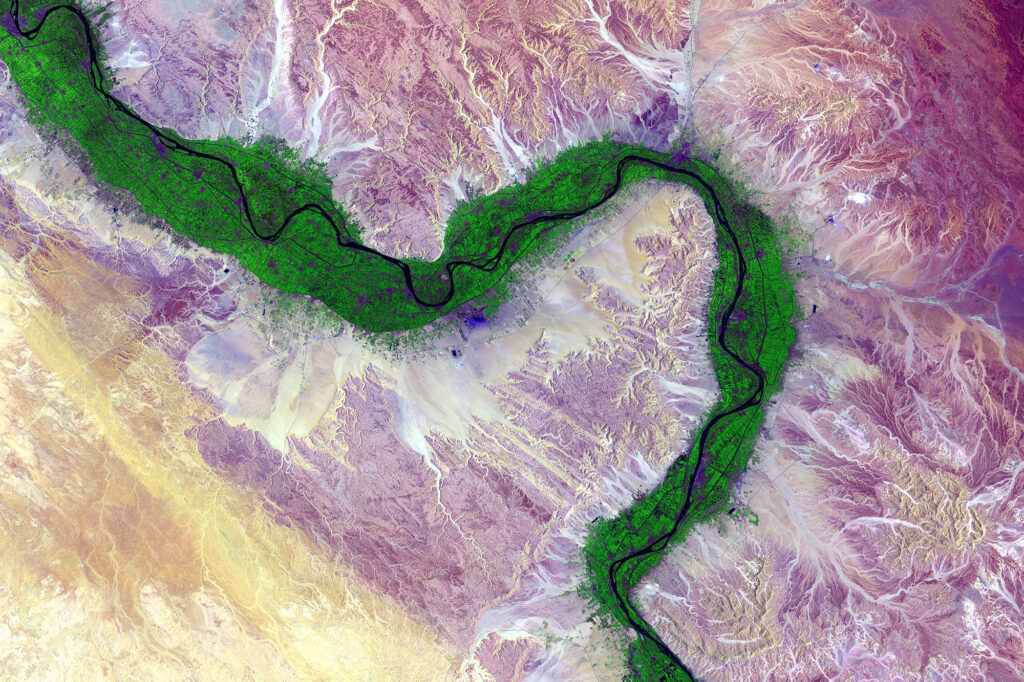
Sudan is geographically located at the crossroads of Sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East and stretches across to the Red Sea. Sudan shares borders with seven countries including Libya and Egypt to the North, Chad to the West, the Central African Republic to the South-West, South Sudan to the South, Ethiopia to the South-East and Eritrea to the East. The White and Blue Niles meet in Khartoum, the capital city of Sudan, and merge to become the Nile River that flows all the way to the Mediterranean Sea via Egypt.
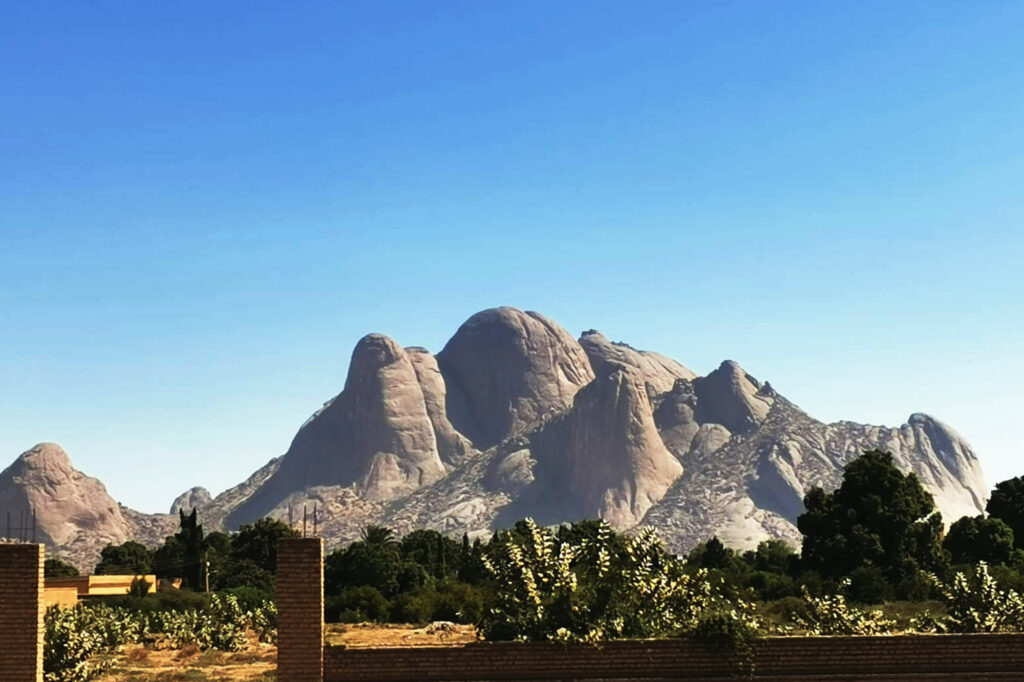
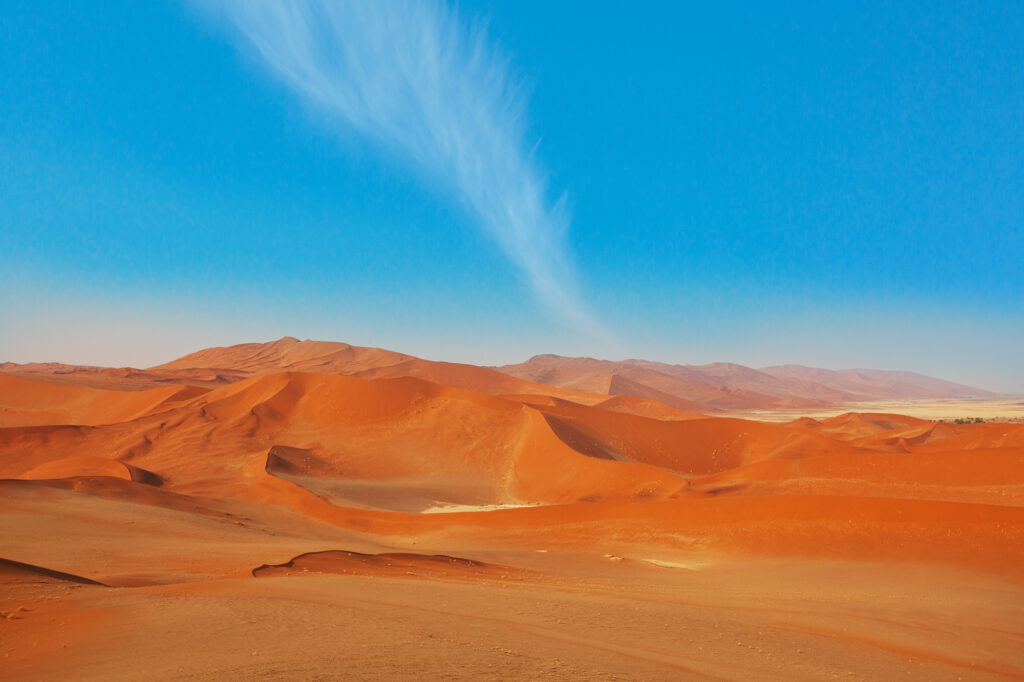
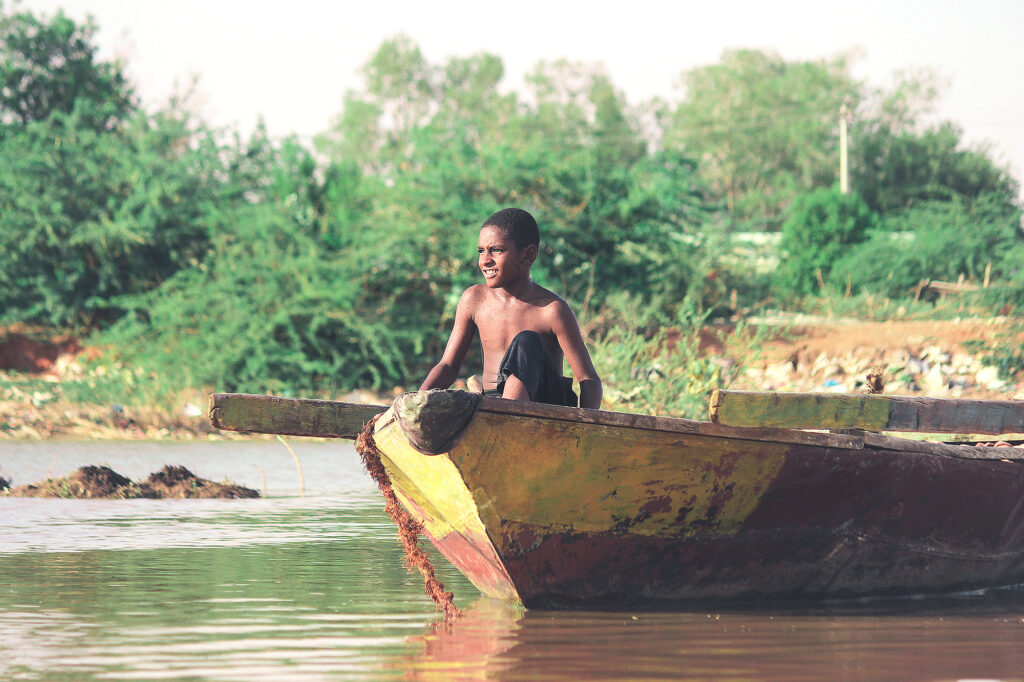
Sudan has a Sahelian belt with the desert in the far north, fertile land in the Nile valleys, the Gezira and across the rest of the country from Darfur to Kassala via Blue Nile and Kordofan States for farming and livestock herding. The River Nile traverses the country from south to north providing a crucial water source, while the Red Sea washes close to 900km of the eastern coast, making Sudan a sea bridge between Africa and the Middle East.
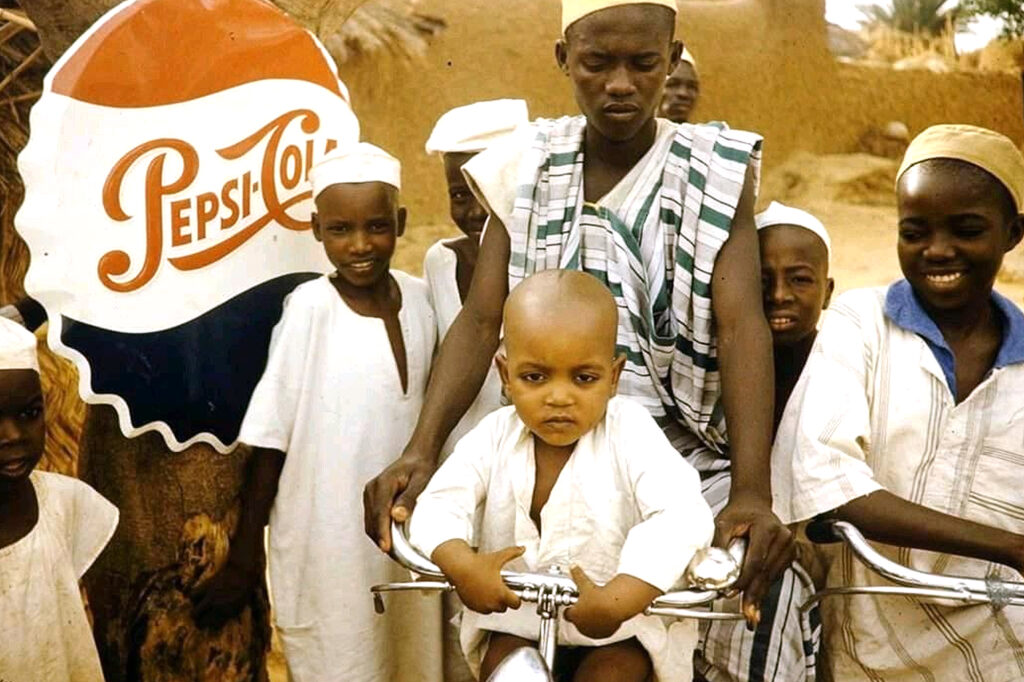
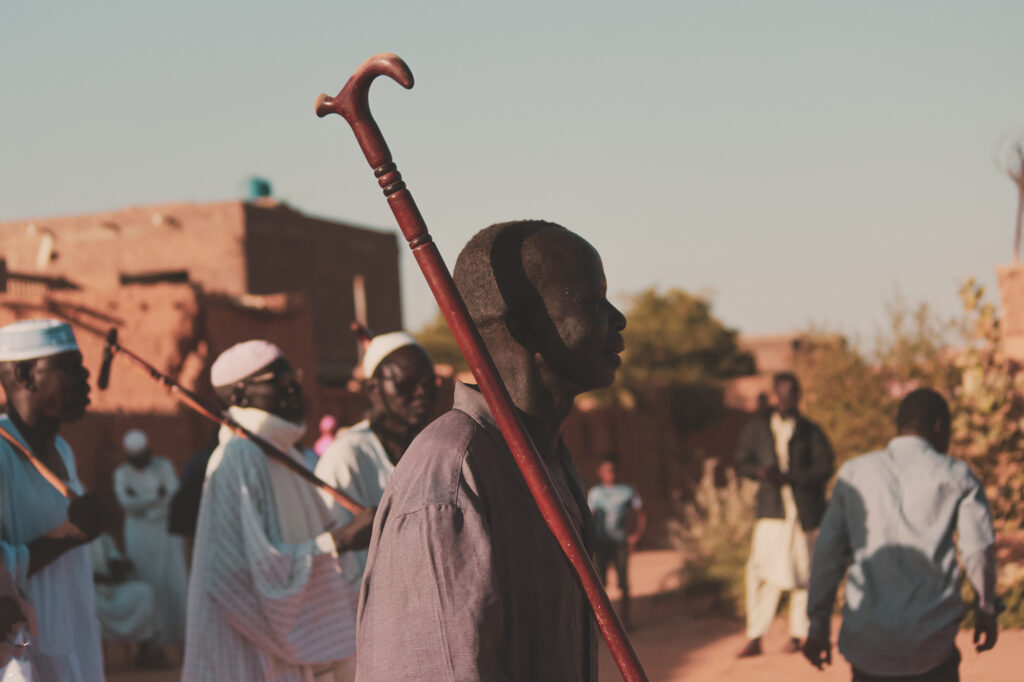
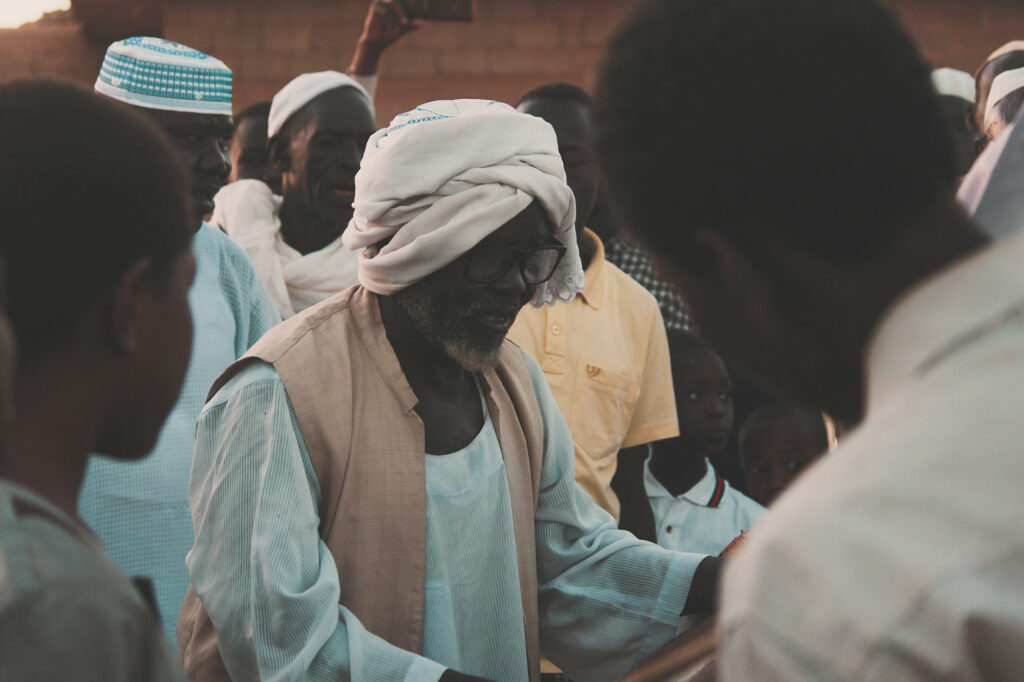
Our people
Sudan is both an African and Arab country, with Arabic being the most widely spoken language. Over 97% of the population are Sunni Muslims with a small Christian minority.
Sudan is growing at a quick rate of 2.42% per year. This rate adds over 1 million people to the population every year. Because the fertility rate is so high, a very large portion of the population is under 15 years old, putting additional strains on social services, especially education and health.
The country is dominated by Muslims, most of whom speak Arabic and are for the most part ethnically mixed. Despite a common language and religion, the people are highly differentiated in their mode of livelihood and comprise city dwellers, village farmers, and pastoral nomads. The tribal system has largely disintegrated in urban areas and settled villages, however, and retains its strength only among the nomads of the plains who raise cattle, sheep, and camels.
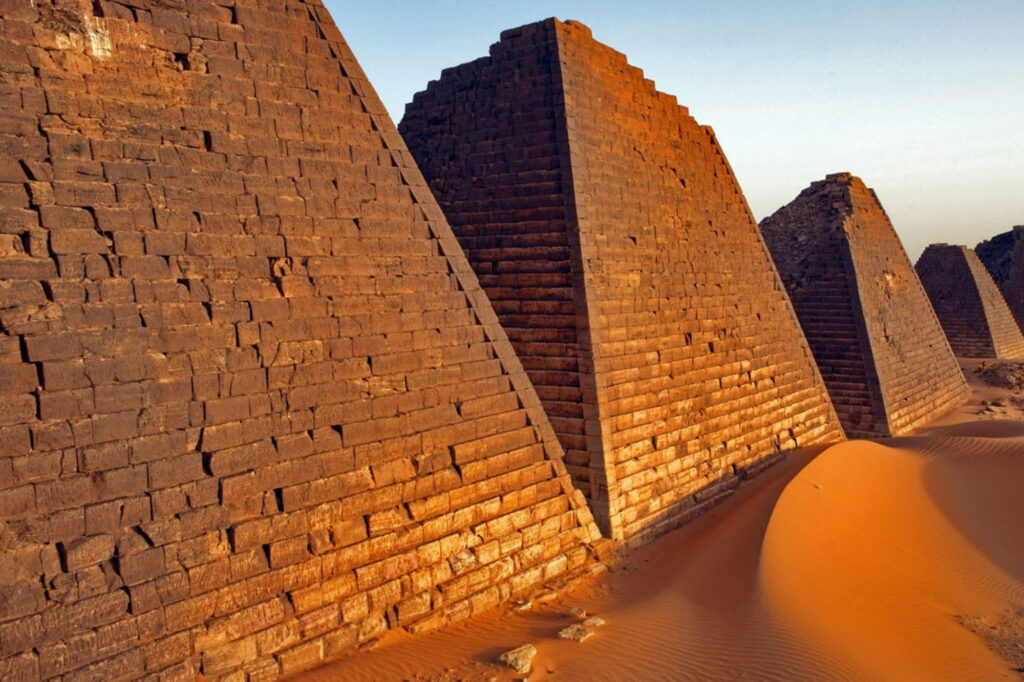
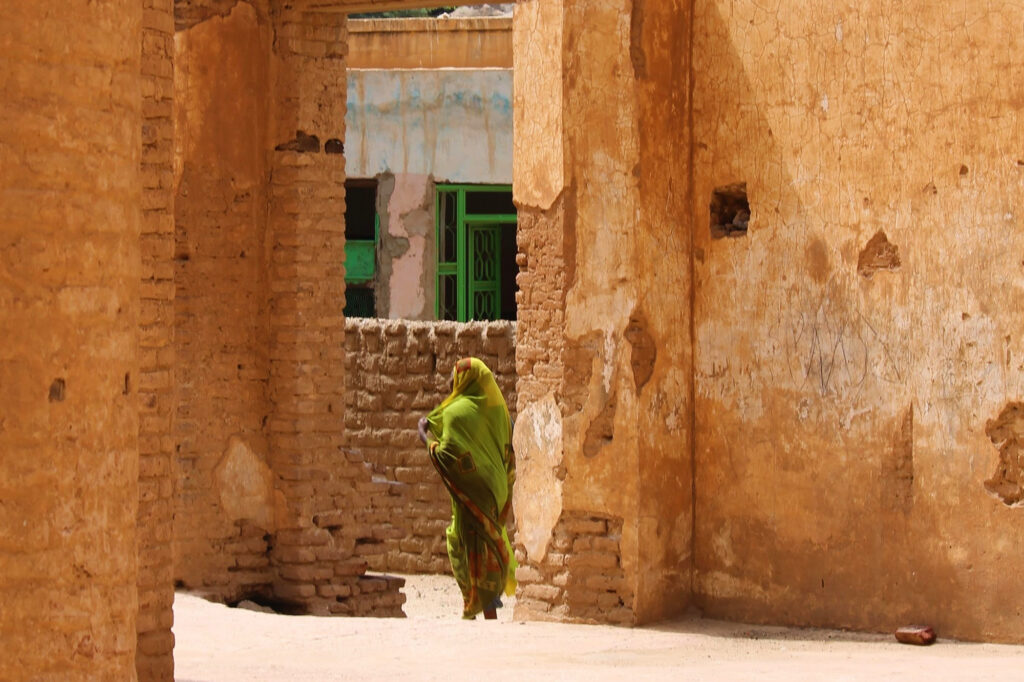
Our culture
There are more than one hundred different indigenous languages spoken in Sudan, including Nubian, Ta Bedawie, and dialects of Nilotic and Nilo-Hamitic languages. Arabic is the official language, spoken by more than half of the population. English is being phased out as a foreign language taught in the schools, although it is still spoken by some people.